
Women at low-risk may be excluded from glucose testing. In all pregnant women, fasting glucose should be measured at the first prenatal visit (no later than 20 weeks' gestation).Ī 75-g OGTT should be performed if the fasting glucose concentration is greater than 85 mg per dL (4.7 mmol per L).Īll pregnant women should be screened through history, clinical risk factors, or laboratory testing. There is fair evidence to recommend screening patients with hypertension or hyperlipidemia for type 2 diabetes to reduce the incidence of CV events and CV mortality.Īll adults with a sustained blood pressure of greater than 135/80 mm Hg should be screened for diabetes.Ĭurrent evidence is insufficient to assess balance of benefits and harms of routine screening for type 2 diabetes in asymptomatic, normotensive patients.
If test results are normal, repeat testing should be performed at least every three years.

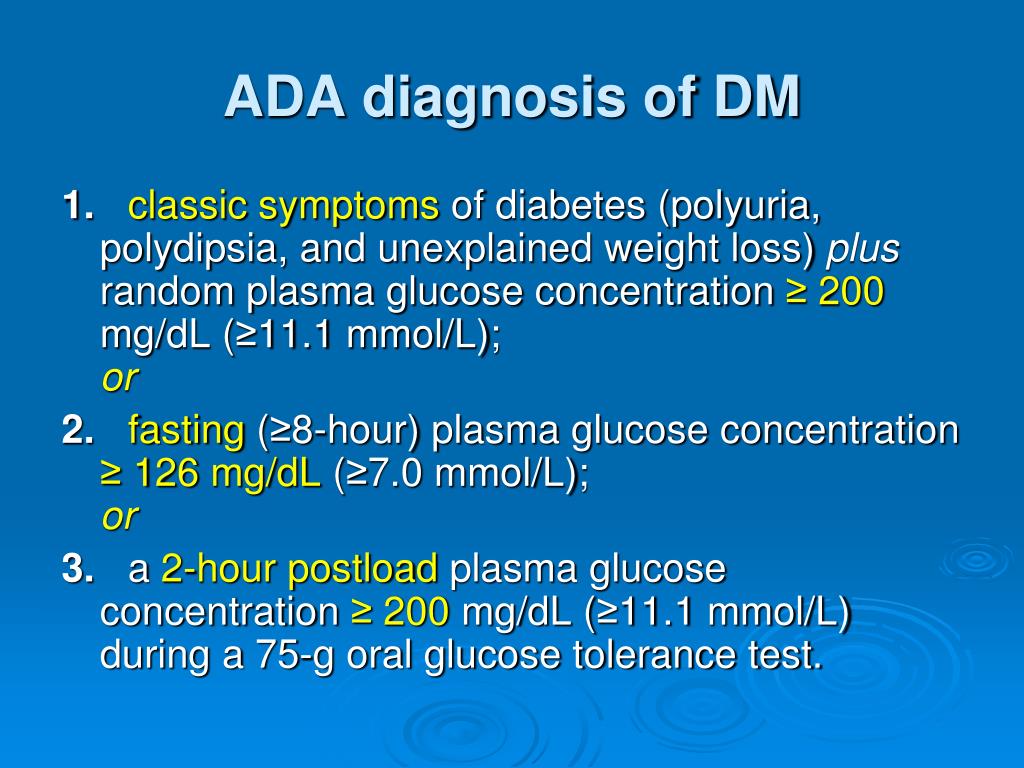
In persons without risk factors, testing should begin at 45 years of age. Testing to detect type 2 diabetes should be considered in asymptomatic adults with a BMI of 25 kg per m 2 or greater and one or more additional risk factors for diabetes.Īdditional risk factors include physical inactivity hypertension HDL cholesterol level of less than 35 mg per dL (0.91 mmol per L) or a triglyceride level of greater than 250 mg per dL (2.82 mmol per L) history of CV disease A1C level of 5.7 percent or greater IGT or IFG on previous testing first-degree relative with diabetes member of a high-risk ethnic group in women, history of gestational diabetes or delivery of a baby greater than 4.05 kg (9 lb), or history of PCOS other conditions associated with insulin resistance (e.g., severe obesity, acanthosis nigricans). PPV of 86 percent for requiring insulin at three years in persons 15 to 34 years of age 26Īll persons 30 years or older who are at risk of having or developing type 2 diabetes should be screened annually. PPV of 75 percent for requiring insulin at three years in persons 15 to 34 years of age 26ħ5 to 85 percent prevalence in adults and children 21 NPV of 94 percent for requiring insulin at six years in adults 25Ībsence: NPV of 49 percent for requiring insulin at three years in persons 15 to 34 years of age 26Ĥ0 percent prevalence in adults and children 21 Presence: PPV of 92 percent for requiring insulin at three years in persons 15 to 34 years of age 26 1.51 ng per mL: NPV of 96 percent for diagnosis in adults and children 20Ħ0 percent prevalence in adults and children 21ħ to 34 percent prevalence in adults and children 23, 24 One hour, 180 mg per dL (10.0 mmol per L)ġ40 mg per dL (7.8 mmol per L), confirm diagnosis with 75- or 100-g OGTT Random glucose test: ≥ 200 mg per dL with symptoms Two-hour OGTT (75-g load): ≥ 200 mg per dL (11.1 mmol per L) LADA: increased C peptide, presence of GADA and ICA, tyrosine phosphatase antibody (IA-2), anti-insulin antibody Type 1 diabetes: decreased C peptide, presence of GADA and ICA Two-hour OGTT (75-g load): 140 to 199 mg per dL (7.8 to 11.0 mmol per L)įasting glucose test: ≥ 126 mg per dL (7.0 mmol per L) Categories of increased risk (formerly prediabetes)įasting glucose test: 100 to 125 mg per dL (5.6 to 6.9 mmol per L)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
